If you’re managing social media for your business, it might be useful to know about some of the most surprising social media statistics this year. Here are 10 that might make you rethink the way you’re approaching social media.
Tag Archives: business
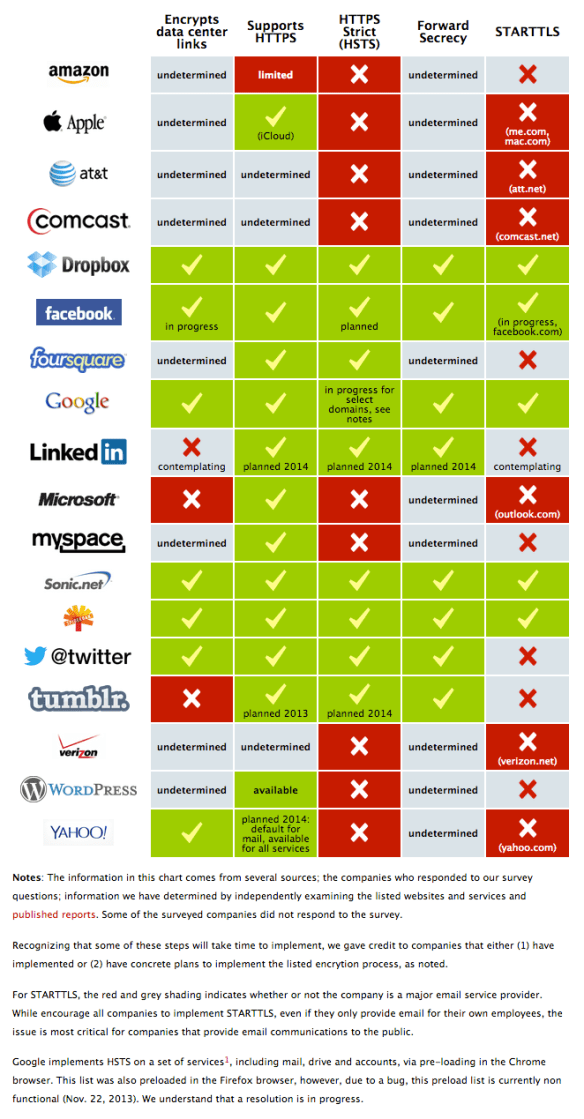
UPDATE: Encrypt the Web Report: Who’s Doing What | EFF
We’ve asked the companies in our Who Has Your Back Program what they are doing to bolster encryption in light of the NSA’s unlawful surveillance of your communications. We’re pleased to see that four companies—Dropbox, Google, SpiderOak and Sonic.net—are implementing five out of five of our best practices for encryption. In addition, we appreciate that Yahoo! just announced several measures it plans to take to increase encryption, including the very critical encryption of data center links, and that Twitter has confirmed that it has encryption of data center links in progress.
Read: UPDATE: Encrypt the Web Report: Who’s Doing What | Electronic Frontier Foundation
Bosses May Use Social Media to Discriminate | WSJ.com
Many companies regularly look up job applicants online as part of the hiring process. A new study suggests they may also use what they find to discriminate.
The study, a Carnegie Mellon University experiment involving dummy résumés and social-media profiles, found that between 10% and a third of U.S. firms searched social networks for job applicants’ information early in the hiring process. In those cases, candidates whose public Facebook profiles indicated they were Muslim were less likely to be called for interviews than Christian applicants. The difference was particularly pronounced in parts of the country where more people identify themselves as conservative. In those places, Christian applicants got callbacks 17% of the time, compared with about 2% for Muslims.
The same experiment, conducted from February to July of this year, found that online disclosures about job candidates’ sexuality had no detectable impact on employers’ early interest.
The research is the latest example of how people’s digital trails can have far-reaching and unintended effects, particularly in the job market.
Read the rest of the story: Bosses May Use Social Media to Discriminate | WSJ.com.
News: Books & Publishing, Music & Film
Books & Publishing
Amazon
- Kindle launches in Australia | The Bookseller
- Digital Census: Tablets closing on Kindle | The Bookseller
- Amazon Updates Fire OS With Deep Goodreads Integration, Better Enterprise Support, “Second Screen” & More | TechCrunch
- Amazon Paperwhite Update Brings Goodreads, Kindle FreeTime & Cloud Collections To E-Reader Owners | TechCrunch
- Vote: What is the best YA novel of all time? The final four | EW
- Nifty Teas Inspired By Classics | BookRiot
- 15 Books That Will Make You A Better Teacher | BuzzFeed
- ‘Masterpiece,’ an Italian Reality Show for Writers | NYT
- Flavorwire: 15 Works of Dystopian Fiction Everyone Should Read and 10 Great Books Contemporary Culture Has Forgotten
- Bowker Names Smashwords as the Biggest Fish in the Indie eBook Publishing Pond | Teleread
- What 20 years of best sellers say about what we read | USAToday
- Price Cuts Bite Into Korean Book Sales, Fixed Price Considered | PublishingPerspectives
- Fans Spend $150K to Help Save a Beloved Indie Comic Publisher | WIRED
- Follett makes 570 redundant | The Bookseller
- Eleanor Catton wins Governor General’s Literary Award | Quill & Quire although Academic calls Eleanor Catton’s Governor General’s win “a literary scandal” | Q & Q
- LGBT: Mari Hannah wins Polari First Book Prize | The Bookseller and Solomon wins Green Carnation | The Bookseller
Music & Film
A Survival Guide for the Newly Unemployed | LifeHacker
Six step survival guide to unemployment. (Note: Some of the resources mentioned are U.S. specific. There are likely comparable services available in your country.)
3 Ways to Use Social Media for Fundraising | See3 Communications
Nice or Tough: Which Approach Engages Employees Most? | HBR
Full Post
It’s probably no news to most people who work that poor leaders produce disgruntled, unengaged employees. Our research also shows convincingly that great leaders do the opposite — that is, that they produce highly committed, engaged, and productive employees.
And the difference is cavernous — in a study of 160,576 employees working for 30,661 leaders at hundreds of companies around the world, we found average commitment scores in the bottom quarter for those unfortunate enough to work for the worst leaders (those leaders who had been rated in the bottom 10th percentile by their bosses, colleagues, and direct reports on 360 assessments of their leadership abilities). By contrast, average commitment scores for those fortunate enough to work for the best leaders (those rated in the 90th percentile) soared to the top 20th percentile. More simply put, the people working for the really bad leaders were more unhappy than three quarters of the group; the ones working for the really excellent leaders were more committed than eight out of ten of their counterparts.
What exactly fosters this engagement? During our time in the training and development industry we’ve observed two common — and very different — approaches. On the one hand are leaders we call “drivers”; on the other, those we call “enhancers.”
Drivers are very good at establishing high standards of excellence, getting people to stretch for goals that go beyond what they originally thought possible, keeping people focused on the highest priority goals and objectives, doing everything possible to achieve those goals, and continually improving.
Enhancers, by contrast, are very good at staying in touch with the issues and concerns of others, acting as role models, giving honest feedback in a helpful way, developing people, and maintaining trust.
Which approach works best? When we asked people in an informal survey which was most likely to increase engagement, the vast majority opted for the enhancer approach. In fact, most leaders we’ve coached have told us that they believe the way to increase employee commitment was to be the “nice guy or gal.”
But the numbers tell a more complicated story. In our survey, we asked the employees not only about their level of engagement but also explicitly, on a scale of one to five, to what degree they felt their leaders fit our profiles for enhances and drivers. We judged those leaders “effective” as enhancers or drivers who scored in the 75th percentile (that is, higher than three out of four of their peers) on those questions.
Putting the two sets of data together, what we found was this: Only 8.9% of employees working for leaders they judged effective at driving but not at enhancing also rated themselves in the 10% in terms of engagement. That wasn’t very surprising to many people who assume that most employees don’t respond well to pushy or demanding leaders. But those working for those they judged as effective enhancers were even less engaged (well, slightly less). Only 6.7% of those scored in the top 10% in their levels of engagement.
Essentially, our analysis suggests, that neither approach is sufficient in itself. Rather, both are needed to make real headway in increasing employee engagement. In fact, fully 68% of the employees working for leaders they rated as both effective enhancers and drivers scored in the top 10% on overall satisfaction and engagement with the organization.
Clearly, we were asking the wrong question, when we set out to determine which approach was best. Leaders need to think in terms of “and” not “or.” Leaders with highly engaged employees know how to demand a great deal from employees, but are also seen as considerate, trusting, collaborative, and great developers of people.
In our view, the lesson then is that those of you who consider yourself to be drivers should not be afraid to be the “nice guy.” And all of you aspiring nice guys should not view that as incompatable with setting demanding goals. The two approaches are like the oars of a boat. Both need to be used with equal force to maximize the engagement of direct reports.
Why Facebook Would Pay $3 Billion for Snapchat (And Why It Shouldn’t) | Wired.com
Facebook just tried to spend $3 billion on a 20-person company that lets you send disappearing photos. At least, that’s the word from The Wall Street Journal, a rather trustworthy source.
According to the paper, SnapChat rejected the offer. But the amazing thing is that Facebook would offer that much money in the first place. SnapChat has no revenues, and its collection of users — however many there are — is puny when you consider that Facebook reaches over 1.2 billion people around the world. Across the internet, so many people are asking themselves: Why on earth would Facebook offer so much for this tiny company?
Read more: Why Facebook Would Pay $3 Billion for Snapchat (And Why It Shouldn’t) | Wired Business | Wired.com.
5 Big Happiness Myths Debunked–And The Power Of Negative Thinking | Fast Company
It sometimes feels as if the “happiness industry”–the self-help books, motivational speakers, corporate consultants and the rest–makes its money by being useless.
It’s an ingenious business model, when you think about it: promise to help people think positive, then when your techniques fail, conclude that they weren’t thinking positively enough–sending them back for more. Among the many myths and misconceptions dogging the subject of happiness, here are five of the worst, along with some suggestions for what to do instead.
Myths debunked:
- It’s Crucial To Maintain A Positive Mindset
- Ambitious Goals, Relentlessly Pursued, Are The Key To Success
- The Best Managers Are Those Who Make Work Fun
- Higher Self-esteem Equals Greater Happiness
- Avoid Pessimists At All Costs
Is It OK to Yell at Your Employees? | Michael Schrage | HBR
Full Article
Steve Jobs. Jeff Bezos. Martha Stewart. Bill Gates. Larry Ellison. Jack Welch. Successful. Visionary. Competitive. Demanding. And each with a well-deserved reputation for raising their voices. They yelled. Yelling was an integral part of their leadership and management styles.
Is that bad? Is that a flaw?
Harvard Business School recently published and popularized a case study of Sir Alex Ferguson, Manchester United’s recently retired manager and the most successful coach in English Premier League history. Ferguson was a fantastic leader and motivator. But Sir Alex was particularly famous for his “hair dryer treatment”: When he was angry with his players, he shouted at them with such force and intensity it was like having a hair dryer switched on in their faces.
Does that make Sir Alex’s leadership less worthy of study and emulation?
Of course, that’s sports. Elite coaches worldwide are notorious for yelling at their talented athletes. Vince Lombardi, Mike Ditka, Bela Karolyi, Pat Summitt, and Jose Mourinho were comparably effective at raising their voices to command attention and results. They inspired great performances and even greater loyalty.
High-decibel intensity is similarly found in special forces training and commands in the military. Yelling is intrinsic to elite military unit culture. It’s expected, not rejected. But perhaps the inherent physicality and emotional stresses of those fields make yelling more acceptable than in more creative and aesthetic endeavors.
But wait: Even the seemingly genteel world of classical music evokes clashes other than cymbals. The world’s best and most highly regarded conductors are frequently famous for raising their voices even higher than their batons. Arturo Toscanini, Herbert von Karajan, and even Daniel Barenboim had reputations for making sure their sharper words were heard above the flatter music. For world-class symphony orchestras, world-class conductors’ critiques are seldom sotto voce.
There’s surely never been a shortage of movie and theater directors who emphatically raise their voices to raise the level of performance of their actors and crew. Neither Stanley Kubrick nor Howard Hawks, for example, were mutes.
What’s true for the collaborative arts holds true for the collaborative sciences, as well. Nobelist Ernest Rutherford was a force of nature who rarely hesitated to firmly and loudly make his questions and concerns known during his astonishingly successful tenure running Cambridge’s Cavendish Lab. His Cavendish was arguably the most important experimental physics lab in the world.
To be sure, yelling doesn’t make someone a better leader or manager. But the notion that raising one’s voice represents managerial weakness or a failure of leadership seems to be prima facie nonsense. The empirical fact pattern suggests that in a variety of creative and intensely competitive talent-rich disciplines around the world, the most successful leaders actually have yelling as both a core competence and brand attribute. These leaders apparently benefit from the acoustic intensity of their authenticity and the authenticity of their intensity.
But is that a good thing? Or a necessary evil?
Stanford Professor Bob Sutton, who authored the managerial cult classic The No Asshole Rule is not quick to condemn leaders and managers who raise their voices with intent.
“To me it is all about context and culture,” he told me via email, “and the history of the relationship. So in some settings, yelling is accepted and is not viewed as a personal insult, but an expected part of leadership. The National Football League is an example… I once tried to teach the ‘no asshole rule’ to a group of folks from NFL teams, and in that context, many of the behaviors that might be shocking in a school, company, or hospital were normal. Much of it comes down to intent and impact, so does it leave the person feeling demeaned and de-energized? Or is it taken as acceptable and expected, and even as a sign of caring?”
Exactly. Would you pay more — and better — attention if you were being yelled at by someone who cares as much about the quality of your work as you do? Or would you find it demotivating? Conversely, if — or when — you raise your voice to a colleague, a boss, or a subordinate, do they hear someone whose passion matters more than their volume?
When I look at the organizations that seem to have the greatest energy and drive, the conversations aren’t whispered and the disagreements aren’t polite. Raised voices mean raised expectations. The volumes reflect intensity, not intimidation.
In other words, yelling isn’t necessarily a bug; it can be a feature — a poignant one.
Sutton concluded his email as follows: “Remember the late and great J. Richard Hackman from Harvard? He yelled at me now and then — I mean yelled, swearing, calling me an idiot — when I was about to make some bad career choices. I appreciated it at the time and have loved him more for it over the years. I knew he was doing because he cared and wanted to make sure I got the message. I wish he were here to yell at me right now.”
If you’re yelling because humiliating and demeaning people is part of who you are, you’ve got bigger professional issues than your decibel level. Your organization needs a quiet conversation about whether your people should work a little louder. But if raising your voice because you care is part of who you are as a person and communicator, your employees should have the courtesy and professionalism to respect that.
Is It OK to Yell at Your Employees? | Michael Schrage | Harvard Business Review